This article is reviewed, corrected, and approved by: Dr. Benjamin McLean M.D. | FCPS | FRCP | MPH
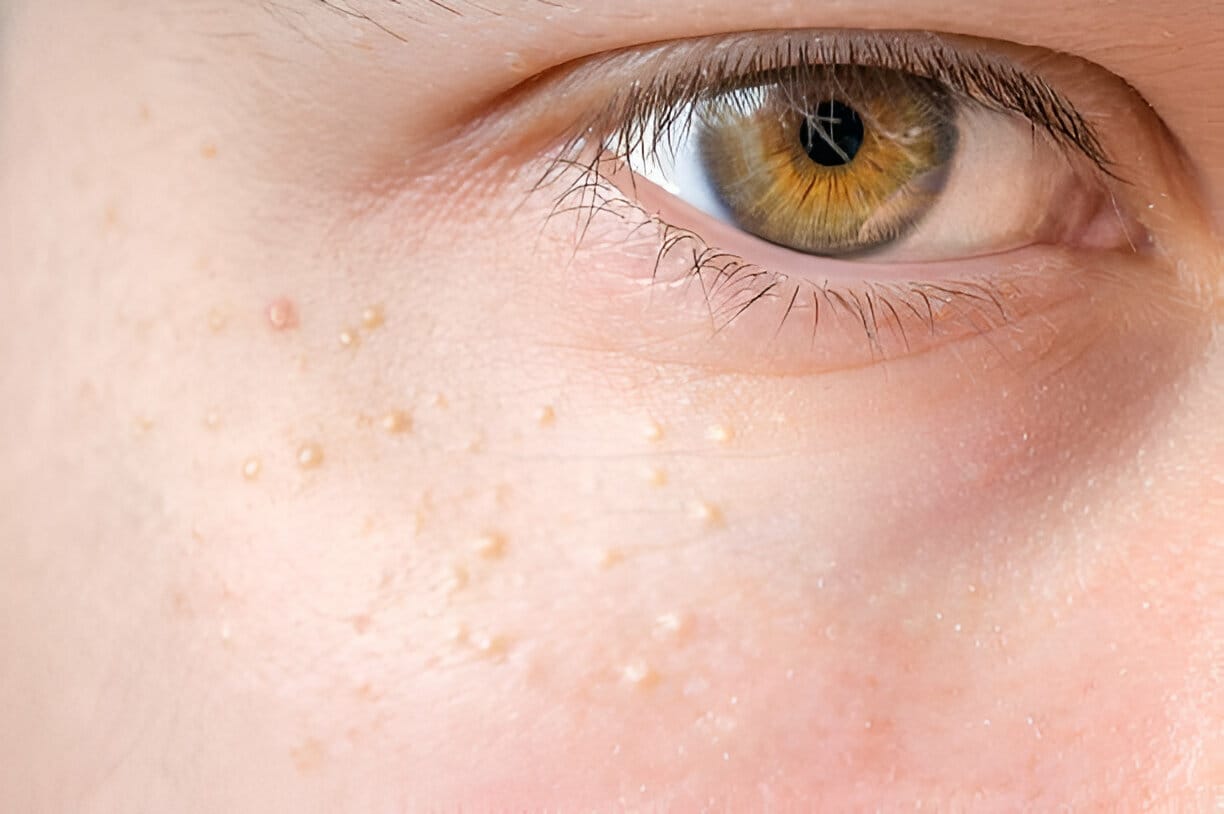
Milia, also known as "milk spots," is a common skin condition that often goes unnoticed and misunderstood. These small, white bumps may appear on the face, particularly around the eyes, nose, and cheeks, but can also occur on other parts of the body. While milia is usually harmless and painless, it can be a nuisance for those who are affected by it.
In this article, we will delve into the details of milia and provide you with all the information you need to understand and treat this condition. From causes and symptoms to prevention and treatment options, we will cover everything you need to know about milia in a clear and concise manner.
By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of what milia is, how to identify it, and how to effectively manage it. So, whether you are someone who suffers from milia or simply curious about this condition, keep reading to learn everything you need to know about milia.
What is Milia and Why Does it Form?
Milia, also known as milk spots, are small, white bumps that commonly appear on the skin, particularly on the face and around the eyes. These cysts form when keratin, a protein found in the outer layer of the skin, becomes trapped beneath the surface, leading to the formation of tiny cysts. While the exact cause of milia is not fully understood, they are often associated with skin damage or trauma, such as burns, blistering, or using heavy skincare products.
Additionally, milia can also develop in newborns and infants due to the immature sweat glands. Despite their harmless nature, milia can be a source of cosmetic concern for individuals, prompting them to seek treatment options for their removal.
Difference Between Milia and Acne
It is important to differentiate between milia and acne, as they have distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Unlike acne, which is primarily caused by excess sebum production and clogged pores, milia are cysts that form when keratin becomes trapped beneath the skin's surface. While acne lesions are often inflamed and can vary in size and appearance, milia appear as small, white or flesh-colored bumps that are typically uniform in size and texture. Milia are not associated with inflammation or infection, unlike acne, which can result in redness, swelling, and pus-filled lesions.
Furthermore, acne commonly occurs in areas with a high density of sebaceous glands, such as the face, chest, and back, while milia are commonly found around the eyes, cheeks, and nose. Treatment for acne usually involves topical and oral medications targeting sebum production and bacterial growth, while milia are typically removed through professional extraction or minimally invasive procedures such as cryotherapy or laser treatment. Understanding the distinctions between milia and acne is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Common Areas for Milia Formation
Milia formation commonly occurs in specific areas of the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, and nose. The delicate skin around the eye area is particularly prone to milia, as it is thinner and more susceptible to trapping keratin beneath the surface. It is not uncommon for milia to cluster around the eyelids, creating small, white or flesh-colored bumps.
The cheeks and nose are also common sites for milia, as these areas can experience a buildup of dead skin cells and keratin. It is important to note that milia can also form in other areas of the body, such as the neck and chest, but their occurrence is less frequent in comparison to the facial region.
Causes and Risk Factors
Milia is a benign skin condition characterized by the formation of small, white or flesh-colored bumps on the skin's surface. While the exact causes of milia formation are not fully understood, there are several known risk factors associated with their development. One common cause of milia is the buildup of dead skin cells and keratin, a protein naturally present in the skin.
This accumulation can clog the pores, preventing the normal shedding of skin cells and resulting in the formation of milia. Other factors that may contribute to the development of milia include excessive sun exposure, certain skin conditions such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis, and the use of heavy or occlusive skincare products. Additionally, newborns often develop milia due to their underdeveloped skin glands, which can lead to the retention of dead skin cells.
While milia is generally harmless and resolves on its own over time, it is important to consult with a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment if necessary.
Who is Most Prone to Milia?
Individuals of all ages and skin types can develop milia, but certain groups may be more prone to its formation. Babies, especially newborns, have a higher likelihood of developing milia due to their underdeveloped skin glands. In these cases, the condition is often temporary and resolves on its own without treatment. Adults with dry or dehydrated skin are also more susceptible to milia, as the lack of moisture can contribute to the buildup of dead skin cells and keratin.
Additionally, individuals who frequently expose their skin to excessive sun or use heavy, pore-clogging skincare products may be at a higher risk. It is important to note that while certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing milia, it can occur in anyone and should be evaluated by a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options and Effectiveness
There are several treatment options available for milia, depending on the severity and location of the condition. One common approach is manual extraction, where a dermatologist or skincare professional uses a sterile needle or blade to carefully remove the cysts. This procedure is typically quick and relatively painless, but should only be performed by a trained professional to minimize the risk of infection or scarring.
Another treatment option is chemical peels, which involve applying a solution containing exfoliating agents to the skin to help remove the build-up of dead skin cells and unclog pores. Chemical peels can be effective in reducing the appearance of milia, but multiple sessions may be required for optimal results. In some cases, topical retinoids or prescription-strength exfoliating creams may be recommended to help speed up the natural shedding of dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your specific case of milia.
Prevention Tips for Milia
To prevent the development of milia, it is important to maintain a consistent skincare routine and follow a few simple guidelines. Firstly, avoid using heavy or greasy skincare products that can clog pores and contribute to the formation of milia. Opt for non-comedogenic or oil-free products that are specifically formulated for your skin type.
Additionally, gently exfoliate your skin regularly to remove dead skin cells and prevent the build-up that can lead to milia. However, be cautious not to over-exfoliate, as this can cause irritation and potentially aggravate the condition. It is also important to protect your skin from excessive sun exposure by wearing sunscreen with a high SPF and seeking shade during peak hours. Lastly, avoid picking or squeezing milia, as this can lead to scarring and further inflammation. By following these prevention tips, you can reduce the likelihood of developing milia and maintain healthy, clear skin.
How Long Does Milia last?
The duration of milia can vary from person to person and depends on various factors. In most cases, milia will resolve on its own over time without any treatment. However, the exact length of time it takes for milia to disappear can range from a few weeks to several months.
If milia persist or become bothersome, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and potential treatment options. Dermatologists may suggest procedures such as extraction, chemical peels, or laser therapy to expedite the removal of milia.
It is important to note that these procedures should only be performed by a trained professional to minimize the risk of complications or scarring. Overall, the duration of milia can be influenced by individual factors and seeking professional advice can help in managing and resolving the condition effectively.
When to See A dermatologist
If you are experiencing persistent or recurring skin issues, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. While mild cases of milia often resolve on their own, there are certain instances when it is essential to seek professional care. If you notice a sudden increase in the number of milia, particularly in areas such as the eyelids or genital area, it is recommended to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist.
Additionally, if you have attempted at-home remedies without improvement or if the milia become inflamed, red, or painful, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A dermatologist can accurately diagnose the condition and provide appropriate treatment options that are tailored to your specific needs. Remember, early intervention and expert guidance can help prevent potential complications and ensure the health and appearance of your skin.
Myth vs Reality About Milia
Milia, commonly referred to as "milk spots," are small, white bumps that often appear on the skin, especially on the face. There are several myths surrounding the causes and treatment of milia that need to be addressed. One common misconception is that milia are caused by poor hygiene or clogged pores, when in reality, they are actually caused by trapped keratin beneath the surface of the skin.
Another myth is that exfoliating or scrubbing the affected area vigorously will eliminate milia. However, this can actually lead to skin irritation and worsen the condition.
It is important to understand that milia cannot be easily removed at home and attempting to do so may result in scarring or infection. Professional intervention, such as that of a dermatologist, is often necessary to safely and effectively treat milia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Milia may seem like a pesky and unsightly skin concern, but with the right knowledge and care, it can easily be managed. Remember to always consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment options. With a consistent skincare routine and healthy habits, you can prevent and reduce the appearance of Milia and maintain a clear, glowing complexion. Stay informed and don't be afraid to seek professional advice when it comes to your skin health.