This article is reviewed, corrected, and approved by: Dr. Benjamin McLean M.D. | FCPS | FRCP | MPH
Cervical cancer usually grows anywhere in the cervix. The cervix is a part between the vagina and the womb or uterus. An infection causes nearly all cervical cancers from certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
Cervical cancer nowadays has become a very common disease for women in the USA. Each year about 13000 patients are hospitalized for this cancer, and more than 4000 women die due to this cancer.
It is unfortunate that among this rate of dying, most of the patients are black women in the USA. Though it can be prevented by doing the regular cervical screening or pap smear.
And with all the medical privilege, these young women tend to ignore pap smear in their early 20s. As a result, at their age of mid 40 or mid 50 their urologist discovered they had symptoms of cervical cancer.
Healthy Cervix
Women want to have a healthy cervix. It should be their health agenda. The cervix may be pink, smooth, uneven, rough, or splotchy.
All of these are signs of a healthy cervix. When women get pregnant, the cervix might have a bluish tint. Also, the cervix can be changed while women are in menopause or breastfeeding their child.
A regular check-up can help you determine whether you have any health problems, such as dysplasia or cancer in your cervix.
A Common Question: How Long Can You Have Cervical Cancer Without Knowing?
Many women have this question that, how fast does cervical cancer grow? Well, it has no specific answer.
This cancer develops very slowly, and it can take years to discover the abnormal changes in the cervix, which becomes intrusive cancer cells. Cervical cancer may develop faster in people with weaker immune systems, but it still takes at least 5 years.
Types Of Cervical Cancers
Generally, two types of Cervical Cancer are diagnosed.
Squamous cell carcinoma
This starts in the plane cells lining the outer part of the cervix. Most cervix cancer is Squamous cell carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma
This begins in the column-shaped epithelial cells that line the cervical canal.
How I Knew I Had Cervical Cancer?- Symptoms To Look Out For
After cervical cancer diagnosis, in the early stage of cervical cancer, you probably don’t experience any symptoms. But do check these early signs and cervical cancer symptoms below. These early symptoms of cervical cancer will help young women to diagnosed as early as possible.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Spotting between period circles
- Bleeding after intercourse
- Longer and heavier menstrual periods
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Excruciating pain during sexual contact.
- Unusual pain while vaginal bleeding.
- Bleeding after a pelvic exam
- Bleeding after starting the menopause
- Irritation while urinating
- Having bowel movements
- Swelling of the legs or abnormal cells in the cervix area.
- Heavy bleeding with pain.
- Unexplained pain in your pelvis or back.
Make an appointment with a doctor to get a best treatment if you face these situations more than once.
Five Warning Signs Of Cervical Cancer

- Itching or burning sensations in the vagina
- Low back or abdominal pain
- Unexplained fatigue
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Abdominal bloating
- Swelling of the legs
- Blood in the urine
large but rather large solid mass in ovary.
Causes And Risk Factors For Cervical Cancer

The HPV - Human Papillomavirus is the primary reason for cervical cancer. Almost 99% of cervical cancer happen because of this. HPV is spread through unprotected sex and other skin-to-skin contact.
However, there are some risks involved with this cancer. These are
- Contracting herpes or chlamydia.
- Smoking.
- Unprotected sex at a very young age.
- Numerous sex partners.
- Not taking routine pap test.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Skin-to-skin contact with anybody who’s considered high-risk for HPV
- Getting pregnant at a very young age.
- More than three terms of pregnancies.
The most dangerous risk factor is unprotected sex. When you go through any kind of unprotected sex, the risk of HPV and other STIs goes up.
Moreover, people with less immunity might get affected by HPV and cervical cancer faster than others who have strong immunity.
Prevention From Cervical Cancer
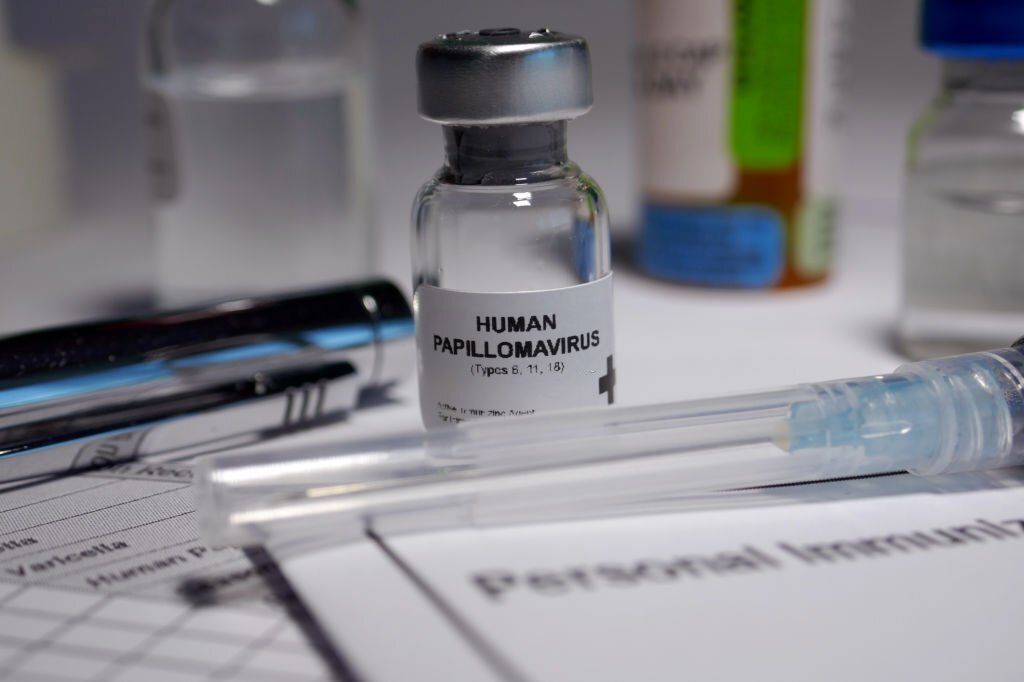
Prevention is the best way to stay away from cervical cancer. To get a healthy cervix, you should do the following-
Get A HPV vaccine
Getting a vaccination will help you to prevent HPV infection and other HPV-related cancers, and this vaccine will keep you away from Cervix cancer as well. Ask your gynecologic oncology doctor whether any HPV vaccine is suitable for you. Also regularly perform HPV test.
Regular Pap tests
Most doctors suggest doing a Pep test at the age of 21 and continuing the test every few years. A Pap test is a simple, safe, and effective way to detect precancerous conditions of the cervix and prevent cervical cancer.
Have safe sex
Avoid unprotected sex. Choose a partner who is healthy and risk-free. And always use condoms to prevent any risk of sexually transmitted diseases, including HPV and cancer.
Quit smoking
Smoking can lead you many health diseases, including the deadly cervical cancer.
Conclusion
The treatment of cervical cancer is quite expensive. If you underestimate the common symptoms at the first stage, then you have to admit to the hospital finally.
Most cervical cancer patients and cervical cancer survivor need to undergo radiation therapy, internal radiation therapy, physical therapy, chemotherapy, and even surgery.
While you have the option not to go to the emergency room or intensive care unit and avoid surgery, then why take risks?
Regular cervical screening and regular pap smears with a gynecologic oncologist can be helpful in the early detection of cervical cancer risk.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question 1 - How To Detect Cervical Cancer At Home?
Answer 1: Usually, your doctor or hospital will test your Cervical center test. But if you wish to do it in private, then you will need to insert a swab a few centimeters into the vagina and spin it for 20 to 30 seconds. Remove the swab, replace it in the packaging bag, seal the whole thing, and submit it to your hospital.
But before doing it by yourself, read the instruction carefully.
Question 2 - Can Anybody Get Cervical Cancer While Pregnant?
Answer 2 - It is rare to get cervical cancer during pregnancy. If it occurs, that means the cancer is in an early stage and may not need to be treated instantly.
However, sometimes the cancer is fast-growing and needs immediate treatment.
Question 3 - What Does Cervical Cancer Smell Like?
Answer 3 - if you have cervical cancer, then you will have a foul smell with abnormal liquid discharge. The discharged thing can be pink, brown, or bloody sometimes.
Even women may feel a simple twinge in their abdominal, and after that, foul-smelling vaginal discharge appears.
Question 4 - Is Cervical Cancer Hereditary?
Answer 4 - Sometimes Cervical Cancer happens due to family medical history. Suppose your mother or sister had cervical cancer. In that case, the chance of developing cervical cancer in your body is relatively high than other women with no blood-related members bearing cervical cancer.
Question 5 - Does HPV Go Away?
Answer 5: In most cases, HPV goes away by itself without any health problems. Maximum within two years, it may go away. And you can be relaxed from the fear of cervical cancer.
But when HPV does not go away quickly, it creates health problems like genital warts and cervical cancer. Genital warts usually appear as a small tumor, bump, swelling, or group of bumps in the genital area.
Question 6: Can You Get HPV Without Having Sex?
Answer 6 - Yes, you can. Women can be infected with HPV without being sexually active. HPV can spread through skin-to-skin contact. Lengthy contact with infected skin, such as holding hands, may cause transmission of the HPV virus.


