Chronic Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) Pneumonia is a rare type of pneumonia that occurs in people with CVID, a primary immune deficiency disorder. People with CVID have a weakened immune system, which makes them more susceptible to infections, including pneumonia.
CVID Pneumonia is caused by a wide range of bacteria, viruses, and fungi and can be difficult to diagnose due to its variety of symptoms, such as fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
Treatment for CVID Pneumonia usually involves a combination of antibiotics and other medications to target the specific organism causing the infection, as well as immune-boosting therapies to help the patient's immune system fight off the infection. CVID Pneumonia can be very serious and, in some cases, life-threatening.
What is CVID Pneumonia?
CVID stands for Common Variable Immune Deficiency, which is a group of primary immunodeficiency disorders characterized by impaired antibody production and increased susceptibility to infections.
Patients with CVID are more likely to acquire pneumonia, which is an inflammation of the lungs that bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms can cause. In people with CVID, the impaired immune system impedes the body's ability to fight these diseases, like interstitial lung diseases and infections, and they are, therefore, more likely to develop severe or recurrent pneumonia.
Symptoms of CVID Pneumonia

Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) Pneumonia is a serious health condition caused by a weakened immune system. It is often associated with interstitial lung disease, recurrent respiratory infections, and inflammation.
Symptoms of CVID Pneumonia may include difficulty of breath, chest pain, fever, fatigue, and cvid lung disease, persistent cough, along with yellow and green mucus. Other signs and symptoms may include wheezing, dry cough, night sweats, and a general feeling of malaise.
Those with CVID Pneumonia may also experience appetite loss, weight loss, and difficulty breathing. It is important that those with CVID Pneumonia seek medical attention promptly.
If left untreated, CVID Pneumonia can progress to a more serious condition and cause serious, long-term health complications. Individuals with CVID, cvid, and fatigue are more common, especially when compared to people receiving SCIG as opposed to IVIG.
Common symptoms are:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Abnormal respiratory sounds when listening with a stethoscope.
Is CVID pneumonia related to covid?
However, CVID is not specified as directly related to COVID-19 (novel coronavirus disease), which is caused by the SARS-cov-2 virus. Individuals with CVID are more susceptible to infections and may have a more severe course of illness if they contract COVID-19, but COVID-19 pneumonia is not the same as pneumonia that can occur in individuals with CVID.
It is important for individuals with CVID to take all necessary precautions to protect themselves from COVID-19, such as getting vaccinated, wearing masks, and practicing good hand hygiene.
Diagnostic Process for CVID Pneumonia
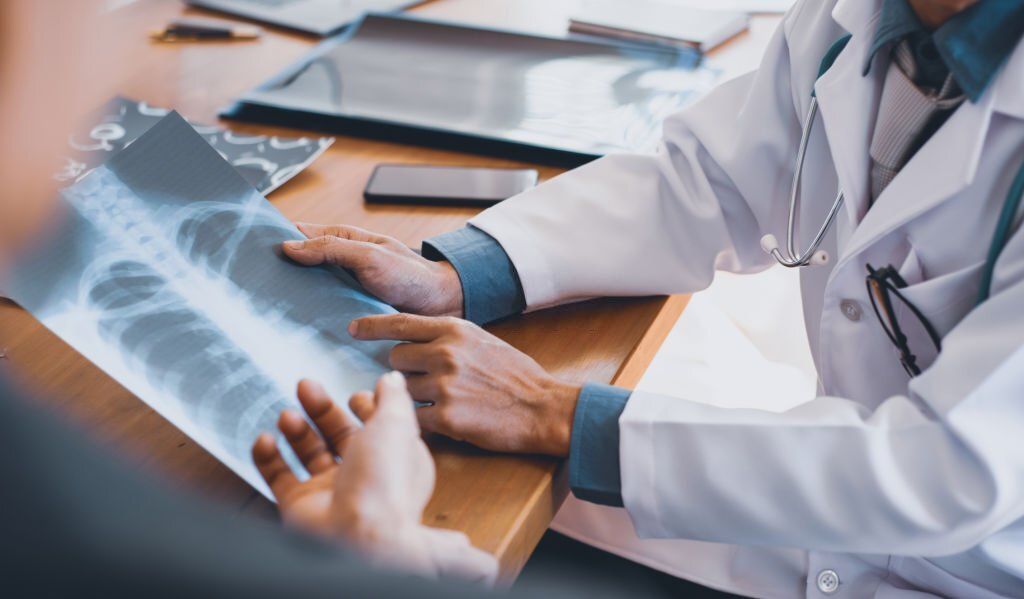

The diagnostic process for CVID Pneumonia typically involves a physical examination, laboratory testing, pulmonary function tests, and imaging. A complete blood count (CBC) can detect a decreased number of white blood cells, plasma cells, and an increased number of lymphocytes, which can be indicative of CVID Pneumonia.
A culture from the sputum may also be taken to help diagnose CVID Pneumonia. Radiographic imaging, such as chest X-rays or computed tomography scans, may be used to detect the presence of lung infiltrates.
Treatment options for CVID Pneumonia generally include antibiotics, corticosteroids, and immunoglobulin replacement therapy. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to target any potential bacterial infections. Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation, while immunoglobulin replacement therapy is used to replenish the body's supply of antibodies. In severe cases, oxygen therapy.
Treatment of CVID Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a medical problem that can be life-threatening and needs to be treated quickly and effectively. CVID pneumonia typically involves a combination of antibiotics, immunoglobulin replacement therapy, open lung biopsy, and supportive care.
When it comes to bacterial pneumonia, intravenous antibiotics are typically the initial treatment approach. The choice of antibiotics prescribed will depend on the particular bacterial strain causing the infection, as well as the patient's age, general health, and past use of antibiotics.
Recovery from an infection may be aided by immunoglobulin replacement treatment. This therapy is typically given intravenously and may be administered on a regular basis to prevent future infections.
In addition to these specific treatments, patients with CVID pneumonia may require supportive care, such as supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or hospitalization. The severity of pneumonia and the overall health of the patient will dictate the level of care required.
Treatment for CVID pneumonia should be initiated as soon as possible to minimize the chances of any complications occurring and improve the chances of a successful outcome. If you have been diagnosed with CVID pneumonia or are experiencing symptoms such as persistent cough. If you have a fever and shortness of breath, you should seek medical assistance immediately.
Finally, treatment of CVID pneumonia typically causes antibiotics to treat the bacterial infection at the root of the problem, as well as other treatments to help manage the symptoms and keep problems from happening.
In some cases, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or other immunoglobulin replacement therapies may also be used to assist in enhancing the immune system and lowering the likelihood of recurring infections.
Prevention of CVID Pneumonia
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a type of primary immunodeficiency disorder that affects the body's ability to fight infections. People who have CVID are more likely to get pneumonia, which is an infection of the lung. To prevent pneumonia in people with CVID, the following steps may be helpful:
- Vaccination: Regular vaccination against pneumococcal and influenza infections is important to reduce the risk of pneumonia.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Hand washing and covering your mouth when coughing helps prevent pneumonia.
- Avoiding exposure to people with infections: People with CVID should avoid close contact with people who have infections, especially respiratory infections.
- Eating a healthy diet (cvid diet): Consuming a well-balanced diet that contains vital nutrients such as vitamins and minerals can enhance the immune system and reduce the risk of contracting pneumonia.
- Exercise: Regular exercise has been found to improve lung function, help to reduce chronic lung disease, and reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Regular medical check-ups: Consult with a doctor or an immunologist can help detect and treat infections early, reducing the risk of pneumonia.
If you have CVID, it's crucial to promptly seek medical attention if you experience pneumonia symptoms such as coughing, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Serious consequences can often be avoided with early treatment.
Tips For Managing CVID Pneumonia and Its Mental Health Impact

Mental health challenges are often an adverse effect of CVID pneumonia, so it's important to take steps to manage both physical and mental health symptoms when you are living with cvid. Make sure that you give yourself some time every day to engage in activities that you will feel more relaxed after doing, like yoga, meditation, or breathing mindfully.
Connect daily with family and friends, reach out for emotional support from healthcare providers or counselors, participate in online communities, and access local support groups.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CVID pneumonia is a rare but serious complication of CVID that can lead to severe respiratory illness and even death if left untreated.
If you have signs of CVID pneumonia, you should talk to your doctor. For example, persistent coughing and difficulty breathing, and to get tested if you are diagnosed with CVID. Early diagnosis and treatment can make all the difference in preventing severe complications and increasing your chances of a full recovery.
F.A.Q
Q: What is cunningham rundles c?
Ans: Cunningham-Rundles syndrome (CRS), also known as immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM type 2 (HIGM2), is a rare genetic disorder that affects the immune system.
Q: What are the clinical and immunological features?
Ans: Clinical features refer to the symptoms and signs that are present in an individual and can be observed or measured by a clinician.
Q: What is CVID Pneumonia?
Ans: CVID pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID). It may also cause lymphoid interstitial pneumonia-like rare issues. CVID is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that prevents your body from making effective antibodies.
Q: What is CVID Pneumonia?
Ans: CVID is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that prevents your body from making effective antibodies.
Q: What Are the Symptoms of CVID Pneumonia?
Ans: Symptoms of CVID pneumonia vary based on the type and severity of the infection, but common symptoms can include coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain, fever, sweating, and fatigue.
Q: How is CVID Pneumonia Diagnosed?
Ans: Diagnosing CVID pneumonia can involve a physical test and radiology, such as an X-ray or CT scan. Your healthcare provider will also likely take a sample of blood to test for the presence of antibodies that indicate infection by particular microbes, such as viruses or bacteria.
Q: What are the common variables of immunodeficiency icd 10?
Ans: The ICD-10 code for Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) is D80.0.
Q: What are the cvid mortality rate and cvid survival rate?
Ans: The mortality rate of cvid and survival rate (Cvid life expectancy) for CVID vary on the severity and treatment of the condition.
Q: What is Interstitial lung disease (ILD)
Ans: It is a type of lung disorder that affects the interstitium or the cell of the lungs. Inflammation and scarring in interstitial tissues can reduce lung function by impairing oxygen transfer to the bloodstream.
Q: What is recurrent bacterial infections and CVID pneumonia?
Ans: Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a type of primary immunodeficiency disorder that can lead to recurrent bacterial infections, including pneumonia.
Q: How long does covid pneumonia last?
Ans: COVID-19 pneumonia (like pneumonia icd 10) duration depends on individual health conditions. Symptoms might last a few days to a few weeks in moderate instances and several weeks or more in severe cases.
Q: What is hypogammaglobulinemia covid?
Ans: Hypogammaglobulinemia (CVID) is primary immunodeficiency. Hypogammaglobulinemia raises the likelihood of recurring, difficult-to-treat infections. Try to maintain cvid diagnosis criteria given by healthcare professionals.


