This article is reviewed, corrected, and approved by: Dr. Joshua Collins M.D. | MRCP। FRCP
Skin conditions can be frustrating, especially when their symptoms overlap. Scabies and eczema are two such inflammatory skin condition that is often mistaken for each other. However, it's crucial to know the difference between the two to get the right treatment.
Both scabies and eczema are skin conditions that can be quite uncomfortable. They have different causes, symptoms, and treatment options, so it is important to know the differences between them. In this article, I will discuss the differences between scabies and eczema, as well as the treatments available for each condition.
Scabies vs Eczema, What’s the Difference?
Scabies
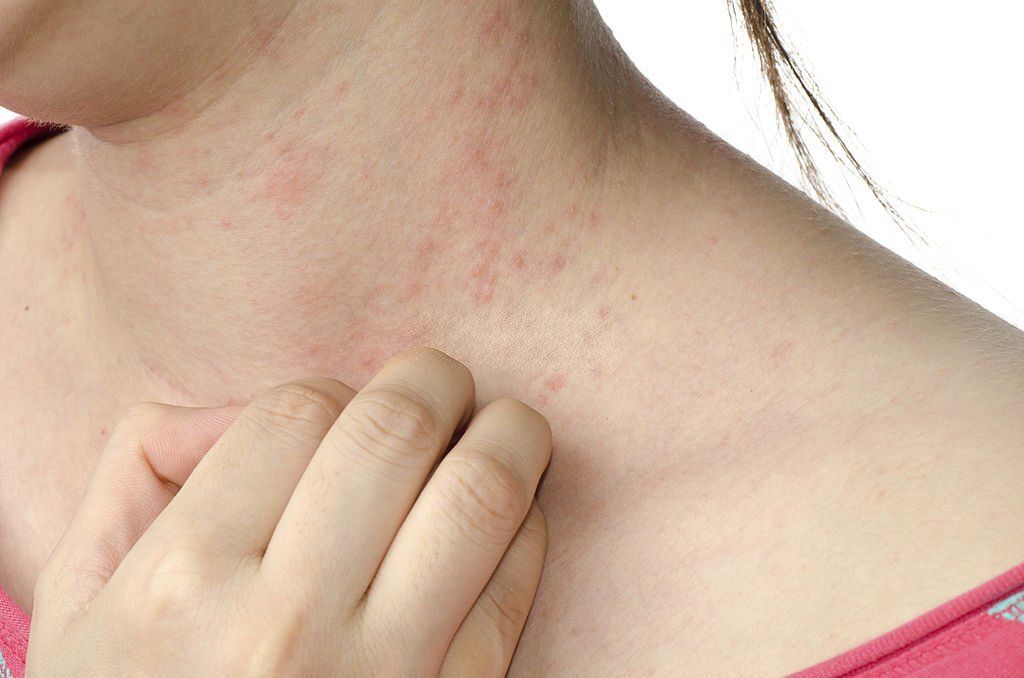
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabies mite, which burrows into the skin, causing itchy rashes. The mites can easily spread from person to person through skin-to-skin contact and sometimes through shared clothing or bedding. Scabies rashes are most common in children and young adults, but anyone can get them due to environmental and genetic factors.
Types of Scabies
Scabies comes in three different varieties, which are categorized by the individual's symptoms and the area of the infection. Here is a quick description of each scabies type:
Classic Scabies
The most typical type of scabies is called classic scabies, sometimes referred to as conventional scabies. It is characterized by severe itching and a skin rash and is brought on by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. It can be extremely itchy and is typically worst at night, making it difficult for people to fall asleep.
The skin creases between the fingers, wrists, elbows, or knees are common places where the rash manifests itself. The scalp, face, neck, and soles of the feet are among additional body regions or itchy patches where they might manifest themselves. People of all ages can have classic scabies, which is very infectious.
Crusted Scabies
Norwegian scabies, also known as crusted scabies, is a severe type of scabies that is most frequently found in patients with compromised immune systems, such as those who have cancer or HIV/AIDS. Crusty scabies is distinguished by thick, crusted, scaly skin and are frequently accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Additionally to the scalp and nails, the infection can spread far and encompass sizable portions of the body. Crusty scabies, in contrast to classic scabies, rarely causes itching. However, it is quite infectious and spreads quickly to other people.
Nodular Scabies
Rarely occurring nodules or little raised lumps on the skin are the hallmarks of nodular scabies. The nodules normally do not hurt and do not itch. Their most frequent locations are the armpits, buttocks, and genitalia.
A hypersensitive reaction to the mites or their byproducts is considered to be the cause of nodular scabies. Older persons and people with compromised immune systems tend to experience it more frequently. Skin-to-skin contact is a highly effective way to transfer nodular scabies, which is also very infectious.
Scabies Symptoms
- Itchy, red rash that may have small, raised bumps or blisters
- Rash may be more severe at night or after a hot shower
- The rash typically appears on the hands, legs spread areas, wrists, elbows, armpits, buttocks, and genitals, but it can appear anywhere on the body.
Scabies Treatment and Prevention
Scabies is a mite infestation of the skin caused by an eight-legged microscopic mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. It causes intense itching and redness, along with rashes, bumps, and blisters. Infected person can spread scabies quickly from person to person through close contact or sharing items like clothing, towels, and bedding.
To prevent the spread of scabies, people should avoid sharing personal items and wash soiled clothing or bedding in hot water. To treat scabies, an over-the-counter cream like permethrin or a spray for scabies can be used to kill mites on the skin's surface. Prescription medications may also be prescribed by a doctor depending on the severity of the infestation.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to help soothe skin irritation and reduce the risk of secondary infections like impetigo. Additionally, soaps for scabies containing sulfur or coal tar can also help soothe itchy, inflamed skin and prevent scars from scabies if applied regularly. You can also use neem oil for getting relief from scabies especially genital scabies like scabies on penis, scabies vagina, etc.
What is Eczema?
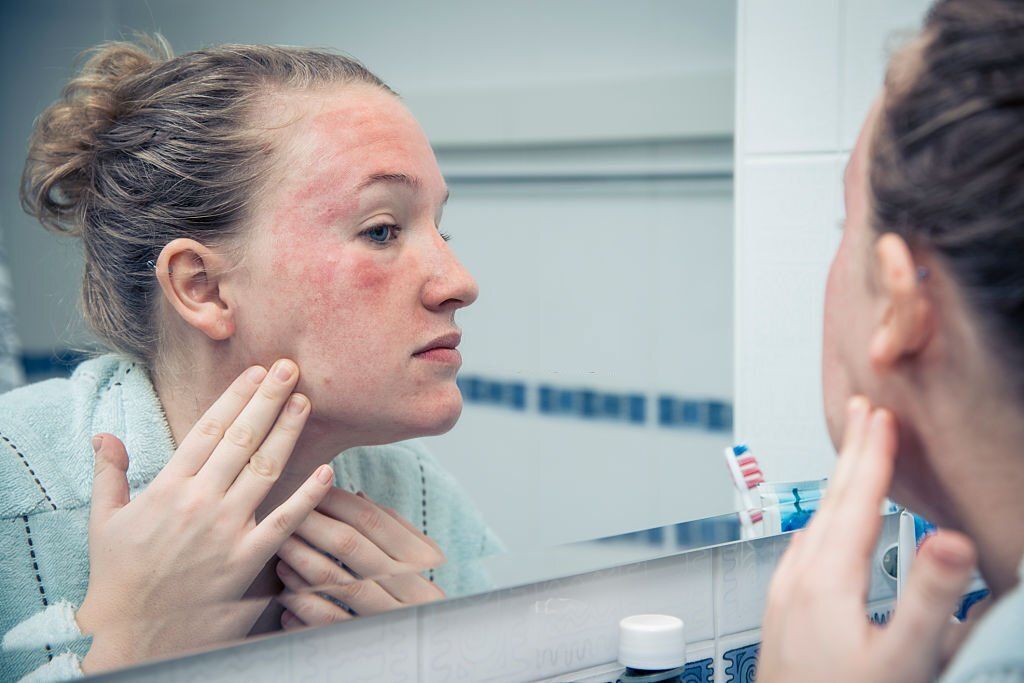

Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflamed, itchy skin. It is often associated with allergies or Asthma, but it can also be caused by genetic factors or environmental triggers. Eczema can affect people of all ages and is not contagious.
Symptoms of eczema include dry, itchy skin and a rash. Rash may appear as red, scaly patches and can be found on various parts of the body, such as the face, neck, inner elbows, and arms. In some cases, small, raised bumps or blisters can appear on your skin when you got eczema.
Types of Eczema
Eczemav is contagious condition that comes in a variety of forms, each with its own traits, causes, and available treatments. Here are the four most common types of eczema:
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic Dermatitis, or atopic eczema, is a chronic condition that affects 1-3% of adults globally and is the most prevalent kind of eczema. It frequently coexists with a family history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever and generally first manifests in early infancy.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis include dry, itchy skin that can also turn red and scaly. It frequently affects the face, neck, and several other body parts, including the hands and feet.
Touch dermatitis
Touch dermatitis is a kind of eczema that develops when an allergy or irritant, such as chemicals, metals, or plants, comes into contact with the skin. A red, itchy rash that may blister or turn crusty is what it looks like.
Acute contact dermatitis is when it manifests quickly and goes away in a few days. Chronic contact dermatitis is when it manifests gradually and lasts for several weeks or months.
Nummular Eczema
Nummular dermatitis or eczema is a kind of eczema that is characterized by scaly, itchy areas of skin that are round or oval in shape. These patches frequently show up on the chest, legs, and arms. Nummular eczema's specific etiology is unknown. However, it might be brought on by dry skin, contact with irritants, or an allergic reaction.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Eczema that affects the hands and feet is known as dyshidrotic eczema. Small, fluid-filled blisters that are itchy and irritable are its defining feature.
These blisters frequently develop on the soles of the feet, the sides of the fingers, and the palms. Although the precise etiology of dyshidrotic eczema is unknown, it can be brought on by stress, allergies, or mental exposure.
Other than these common forms of eczema, there are also some other variants, such as papular eczema and cetaphil eczema.
Prevention and Treatment of Eczema
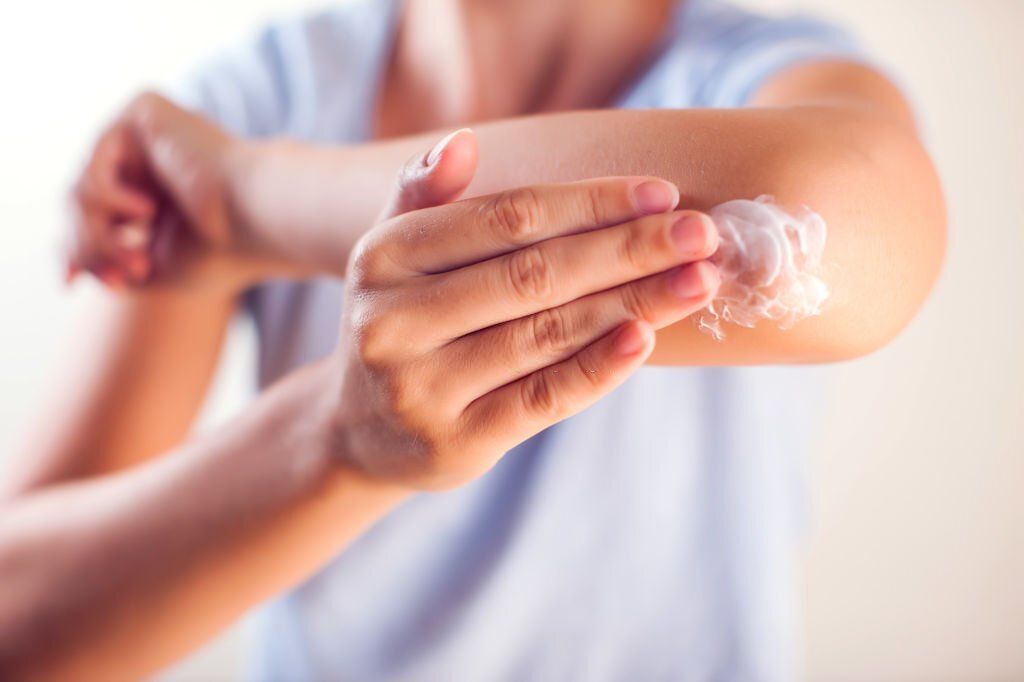

Although there is no known treatment for eczema, there are actions you may take to control the condition's symptoms and stop eczema flare-ups.
Regulate Moisture
Maintaining moisture in your skin is crucial for avoiding eczema. Every day, especially after a shower or bath, apply a fragrance-free moisturizer or oils like oil oregano for eczema, castor oil for eczema to your skin, etc. By doing so, you'll be able to retain moisture and keep your skin from drying out.
Avoid Eczema Triggers
Be aware of the things that cause your eczema, and make an effort to stay away from them. Some meals, stress, detergents, and soaps are typical causes. Eczema patients have an overactive immune system. Avoid harsh chemicals and use soft body scrub for eczema, fragrance-free cosmetics on your skin like oat soap for eczema, etc.
Dress Properly
Choose comfortable, breathable eczema sleeve materials like cotton for your clothes that won't irritate your skin. Wearing wool, synthetic fabrics, and clothing that is too tight might irritate the skin and exacerbate eczema.
Reduce Stress
Stress can cause flare-ups of eczema. Find stress-reduction strategies, such as yoga, meditation, or physical activity. These activities can help you detox eczema-related problems.
Treating Eczema

There are many methods of treating eczema. These methods are discussed below
Topical Steroids
Topical steroids are commonly used to treat eczema. They work by reducing inflammation and itching. Your doctor will prescribe a steroid cream or ointment that is appropriate for your skin.
Moisturizers
In addition to preventing eczema, moisturizers can also help treat it. Apply a thick layer of fragrance-free moisturizer to your skin several times a day, especially after bathing or showering.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines can help relieve itching associated with eczema. They are available over-the-counter or by prescription.
Immunosuppressants
In severe cases, immunosuppressants may be prescribed by your doctor to help reduce inflammation in a person's skin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question 1: Can eczema on the scalp affect hair growth?
Answer 1: Hair loss from eczema can occur due to follicular eczema. When you got eczema on your scalp due to follicular eczema, it can also affect your hair growth.
Question 2: Is scabies an STD?
Answer 2: Because it frequently spreads during intercourse, scabies is sometimes regarded as a STI. But in general, it is not an STD.
Question 3: Does tanning help eczema?
Answer 3: It is obvious that using a sunbed may significantly lessen eczema symptoms as well as post scabies syndrome.
Question 4: How long can scabies live in a mattress?
Answer 4: On a mattress and other inanimate objects, scabies mites can survive for two to three days.
Eczema and scabies are both skin conditions that can cause a lot of discomfort. While they have some similarities, there are key differences between the two conditions.
If you think you might have scabies or eczema, it's important to see a medical professional, so you can get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. With proper treatment, most people with scabies or eczema can find relief from their symptoms and heal their skin.


